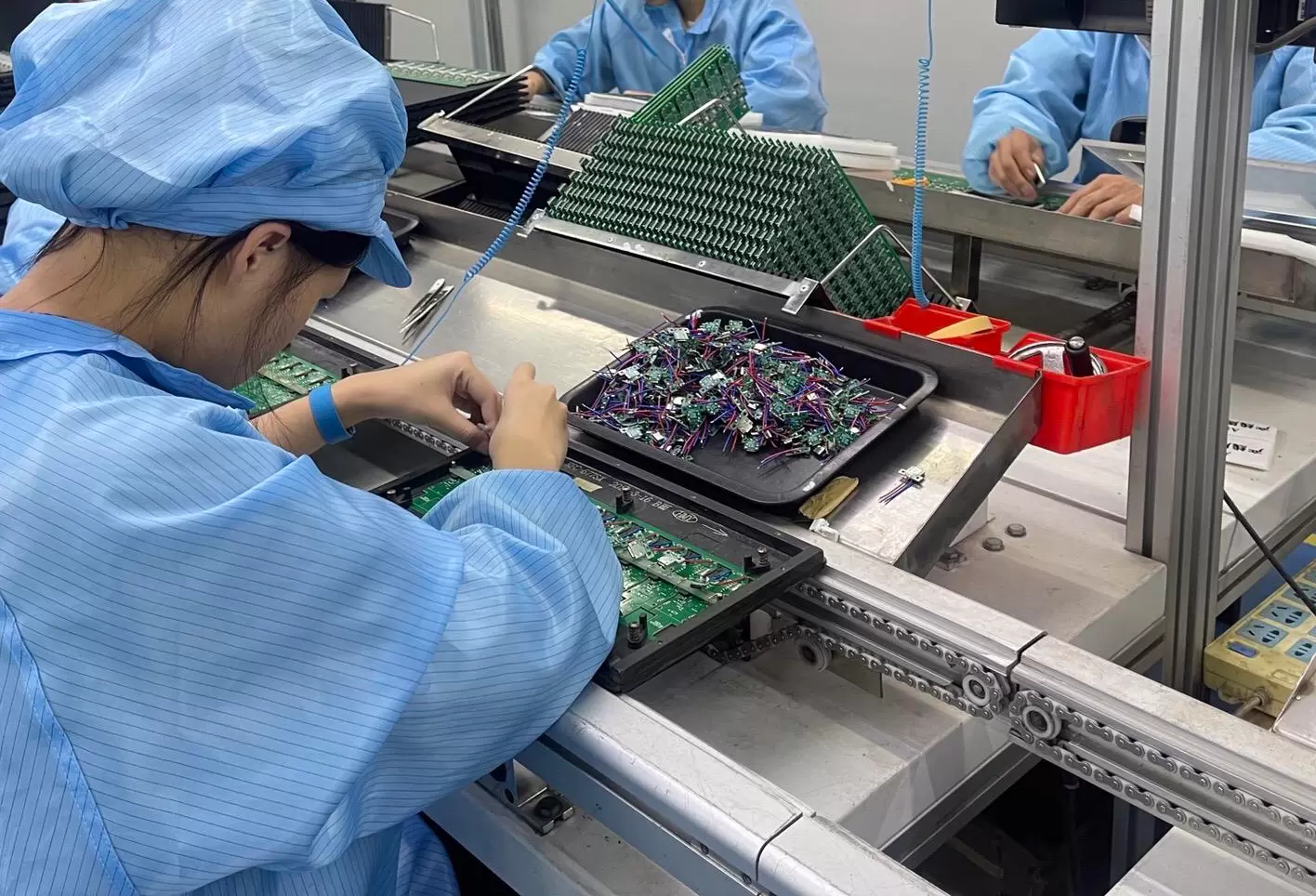
DIP (Dual In-line Package) and wave soldering are essential processes in through-hole PCB assembly. DIP refers to electronic components with two parallel rows of pins, which are inserted into pre-drilled holes on the PCB. These components are widely used for ICs, resistors, capacitors, and connectors that require strong mechanical stability.
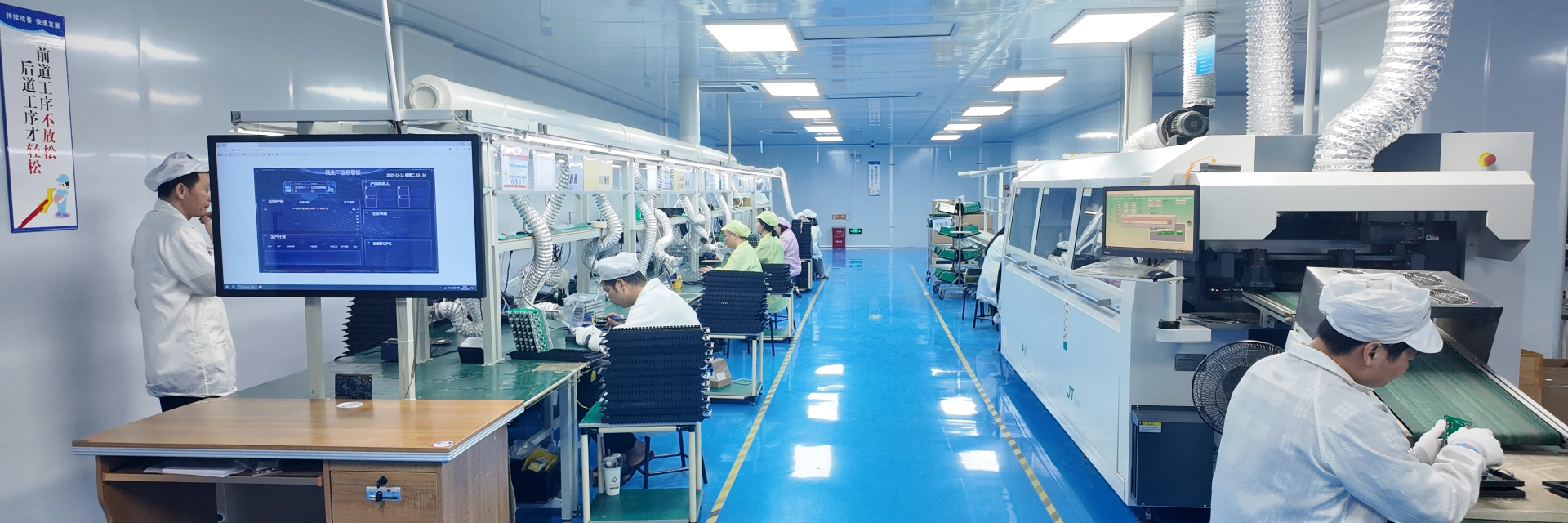
Wave soldering is a high-efficiency soldering method used to attach these through-hole components. During the process, the PCB passes over a wave of molten solder, simultaneously soldering all component pins. Preheating and flux application ensure strong, reliable solder joints and prevent defects like solder bridges or cold joints.
Together, DIP insertion and wave soldering provide a robust and efficient solution for through-hole PCB assembly, balancing production speed with high reliability.


 en
en





 WhatsApp
WhatsApp