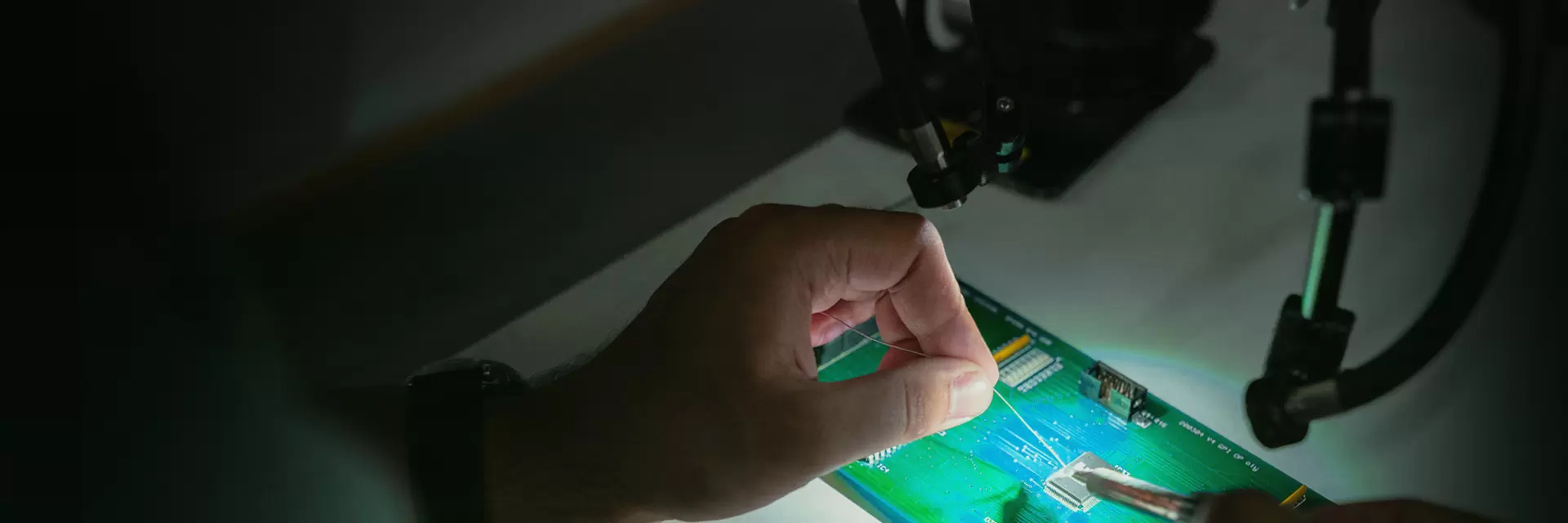
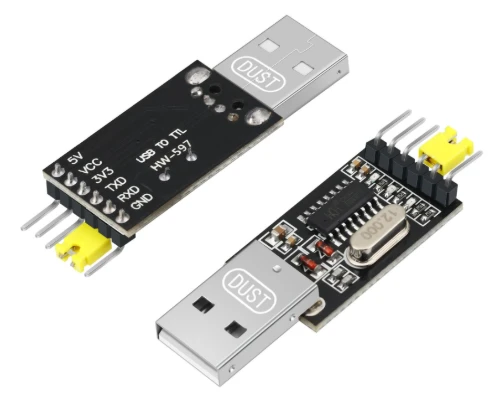
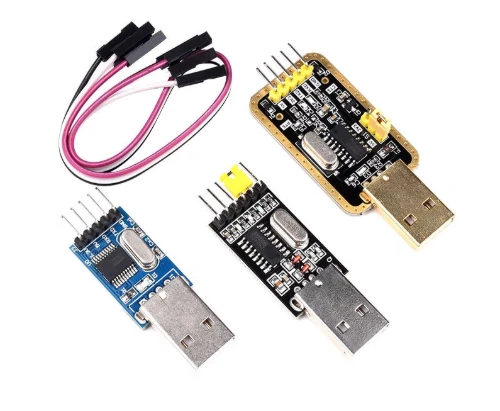
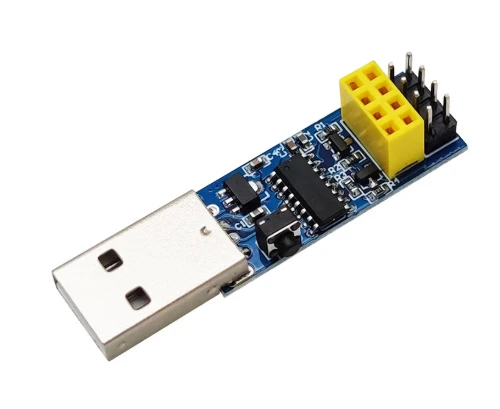
Firmware flashing is the process of transfering the firmware into MCU/Microcontroller/Chip by certain software which issued from MCU manufacturers, such as STmicroelectronics, Atmel, Arduino and Espressif, by dedicated tools like programmer(USB-TTL,etc) or a flash programming fixture for production.
As a One-stop manufacturer, Benlida also provides the service to flash the firmware into the PCBA boards, then go for next step: functional testing.
If you need this service, please consider to provide firmware, operation instruction/guide to us, then we will do before functional testing.

 en
en
























 WhatsApp
WhatsApp