Comprehensive Overview for LED PCB
LED PCB is printed circuit board which carries and power light-emitting diodes (LEDs). It is physical platform but also crucial for LED performance, lifespan, and reliability. In this article, we are going to comb the cores of LED PCB, related notes and applications.
1. Core Characteristics and Requirements of LED PCBs
Due to the certain application of LEDs, the carrier PCBs are different than common PCBs:
● High Thermal Conductivity: When LED emits light, only around 15-25% of its electrical energy would be converted into light and the majority would convert into heat. If heat cannot be dissipated immediately or at least quickly, it will lead to light degradation, color temperature degradation, and shorten lifespan dramatically. Therefore, heat dissipation is the primary consideration on LED PCB.
● High Current Carrying Capacity: Especially for high-power LEDs and LED arrays in high-density, the PCB traces need to be able to withstand large currents and not overheating.
● Considerations of Optical: The PCB layout (LED array, spacing, etc) directly affects the uniformity of light output and optical effects. Sometimes a white or high-reflectivity solder mask is applied, to improve light output efficiency.
● Reliability: LEDs are often applied in environments which requires long-term, continue working (such as lighting and displays), and the PCB must be excellent for thermal resistance, humidity resistance and mechanical strength.
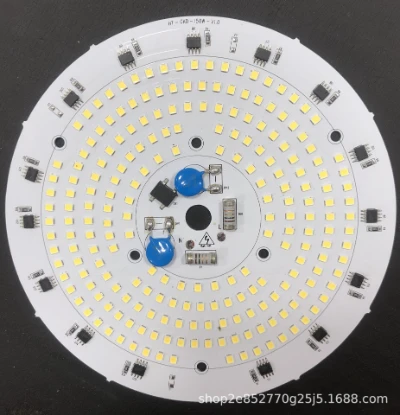


2. Common Types of LED PCBs (catagorized by Substrate Material)
This is the most important way to catagorize LED PCBs, based on heat dissipation and power output.
| Type | Substrate Materials | Characteristics | Applications |
| FR-4 PCB | Glass fiber epoxy resin | Low cost, well-developed technology, but poor thermal conductivity(~0.3 W/mK) | Low-power LEDs, indicator lights, LED strips, general indoor lighting. |
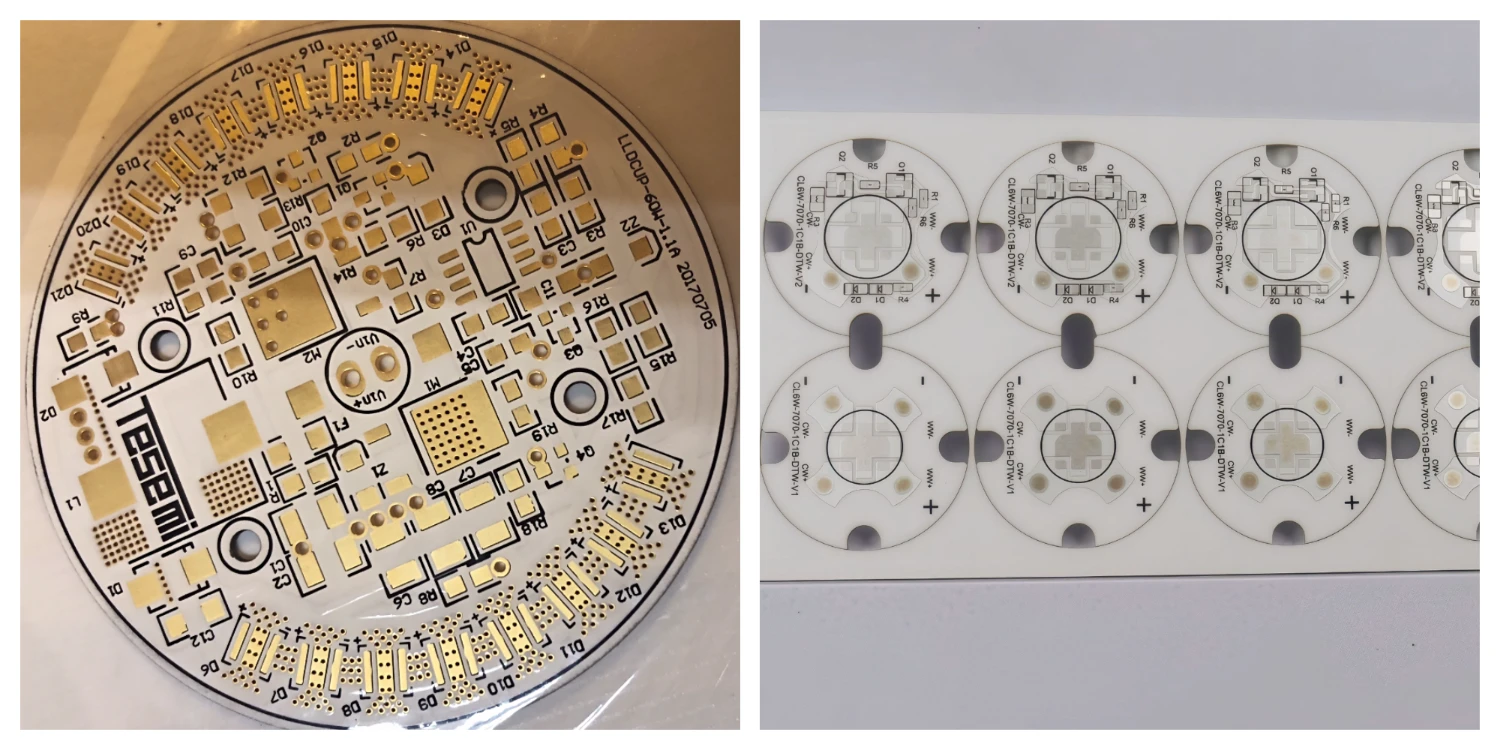
| Metal Substrate PCB | Aluminum (aluminum substrate), sometimes copper. | Excellent heat dissipation (aluminum substrate thermal conductivity 1.0-4.0 W/mK). Structure: copper foil circuit layer + insulating dielectric layer + metal base layer. | The most common option, widely applied for high-power LED streetlights, vehicle lights, high-brightness indoor lighting, stage lights. |
| Ceramic Substrate PCB | Alumina, aluminum nitride, etc. | Excellent heat dissipation (aluminum nitride could reach 170-230 W/mK), high voltage resistance, high temperature resistance, good insulation, but high cost and brittleness. | Ultra-high power LEDs, automotive headlights, LED chip packaging substrates, advanced optical equipment. |
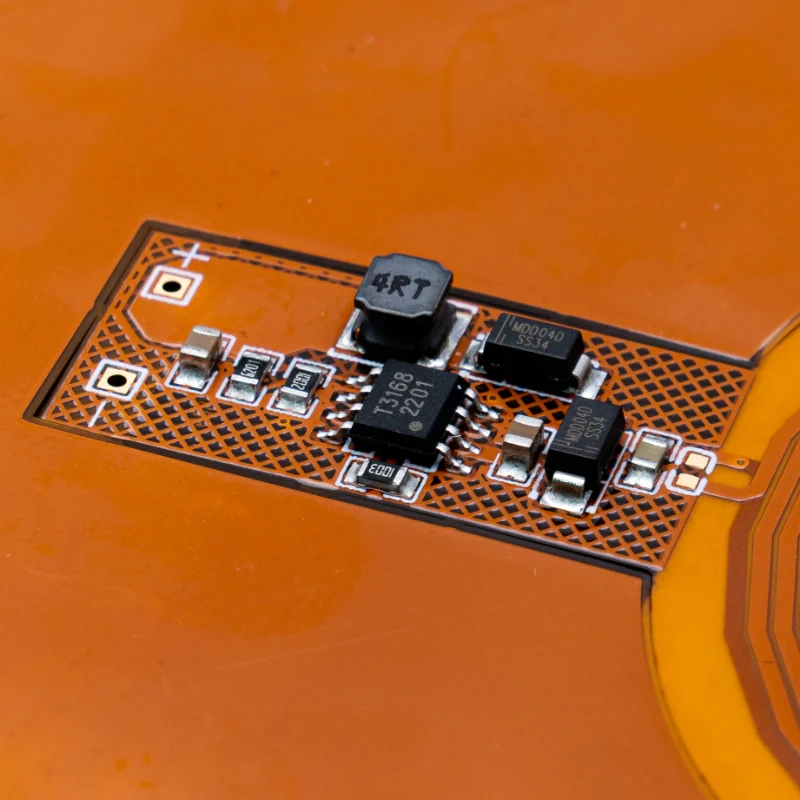
| Flexible PCB | Flexible materials such as polyimide | flexible, bendable and thin. While heat dissipation is generally average, optional and flexible for shapes | Flexible LED light strips, wearable devices, backlight displays, and curve lighting |
| Copper PCBs | Copper | Better for heat dissipation than aluminum substrates, but more expensive and heavier. | Extreme requirements for heat dissipation, such as high-power spotlights. |






3. Key Designs and Manufacturing Processes
1) Thermal Design:
● Thermal Paths: Designing a reasonable heat conduction path to allow heat to travel from the LED chip → pads → PCB copper foil → insulating layer → metal substrate → and finally dissipate into the air through the heat sink.
● Heat Sink/Heat Heatsink: High-power LED PCBs typically require an additional aluminum profile heat sink mounted on the back of the metal substrate.
● Thermal Vias: In FR-4 multilayer boards, an array of thermal vias is used to conduct heat from the front-side LEDs to the underlying copper plane or heat sink layer.
2) Layout and Routing:
● LED Arrays: distribution evenly to avoid localized overheating.
● Trace Width: Calculate trace width, based on drive current, to reduce resistance and heat generation.
● Symmetrical Layout: For multi-LED arrays, design symmetrical to ensure current and brightness.
3) SMT and Soldering:
● Typically LED PCBs apply surface mount technology.
● Reflow soldering is the most commonly applied soldering process. Precise control of the oven temperature is required to prevent LED damage from overheating.
● Pad Design: Conforms to LED package specifications to ensure good solder strength and thermal conductivity.
4) Special Processes (for Metal Substrates):
● V-Cut: Facilitates the separation of multiple small boards from panel.
● Immersion Gold/OSP: Protects solder pads and enhances solderability.
4. Applications
● General Lighting: LED bulbs, panel lights, streetlights, industrial&mining lights.
● Automotive Lighting: Daytime lights, headlights, interior ambient lighting, brake lights.
● Backlighting Displays: LCD backlights for TVs, monitors, and laptops.
● Advertising and Displays: LED displays, advertising lights, and signages.
● Consumer Electronics: Ambient lights, keyboard backlights, and indicator lights on smart home.
● Specialty Lighting: Plant grow lights, medical sterilization lights, and stage lighting.
5. Summary: Designs and Material Selection
1) Power supply level and substrate materials:
< 1W / Low density: FR-4 is optional.
1W / High-density lighting: Aluminum substrate is preferred.
>10W / Extreme environments: Consider ceramic or copper substrate.
2) Define electrical parameters: LED working voltage/current, driving method (constant current/constant voltage), control signals (e.g., PWM dimming, RGB).
3) Systemic Integration of heat dissipation: The PCB must be designed in conjunction with the casing and heat sink, with consideration for thermal interface materials (thermal grease/pads).
4) Optical: The PCB layout must match the optical design of the lens, reflector, or light guide plate&pipe.
5) Supply Chain and Cost: Choose the most cost-friendly solution while good at performance and reliability (aluminum substrates is one of best options).
Trends in Future:
1. Integration: Integrate LED driver chips, control circuits, and LED chips onto the same PCB (e.g., COB packaging), resulting in smaller size and more stable performance.
2. Intelligence: Integrate sensors(lightness, temperature, humidity, RF, radar, etc) and communication modules (IoT, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Zigbee) on the PCB to achieve intelligent dimming, color shift&adjustment, and network control.
3. High Density and Miniaturization: With the development of Mini/Micro LED technology, the technology requirements for PCB would increase significantly, from line accuracy, flatness, and heat dissipation capabilities, require advancements in HDI and special substrate technologies.
In conclusion, LED PCBs are the carrier and intersection of four major factors: optics, electronics, thermodynamics, and mechanics. A successful LED product must own the optimal balance across these four aspects.
Benlida has been manufacturing PCB and PCBA for 14 years, we manufacture various of LED PCB for many customers from domestic to global market. You are welcome to contact Benlida when you need PCB for LED products!

 en
en



 WhatsApp
WhatsApp