Advantages, Disadvantages and Applicationsof Aluminum PCB
Aluminum Printed Circuit Boards (Aluminum PCBs) are a specialized type of PCB that uses aluminum as the base material instead of traditional fiberglass (FR-4). This unique structure—typically consisting of a circuit layer, an insulating layer, and an aluminum substrate—gives them distinct properties suited for specific industrial needs. Below is a detailed analysis of their advantages, disadvantages, and key applications.
Advantages of Aluminum PCB

Excellent Heat Dissipation
Aluminum is a highly conductive material, enabling efficient heat transfer from electronic components (e.g., LEDs, power transistors) to the substrate. This prevents overheating, extends component lifespan, and maintains stable performance—critical for high-power devices.
Lightweight and Durable
Compared to heavy metal substrates like copper or iron, aluminum is lightweight, reducing the overall weight of electronic devices. Additionally, it offers strong mechanical strength, resistance to corrosion (with proper surface treatment), and durability against vibrations or shocks, making it suitable for rugged environments.
Cost-Effective
Aluminum is more affordable than precious metals (e.g., copper) while providing better heat dissipation than FR-4. This balance of performance and cost makes aluminum PCBs a cost-efficient choice for mass-produced electronics.
Simplified Manufacturing
Aluminum substrates are easier to cut, drill, and shape than rigid FR-4 or metal-core PCBs, streamlining the manufacturing process. They also support automated assembly (e.g., SMT) and can be integrated with heat sinks or cooling fins for enhanced thermal management.
Environmental Friendliness
Aluminum is recyclable, aligning with sustainability goals. Its long lifespan and resistance to degradation also reduce electronic waste compared to less durable PCB materials.
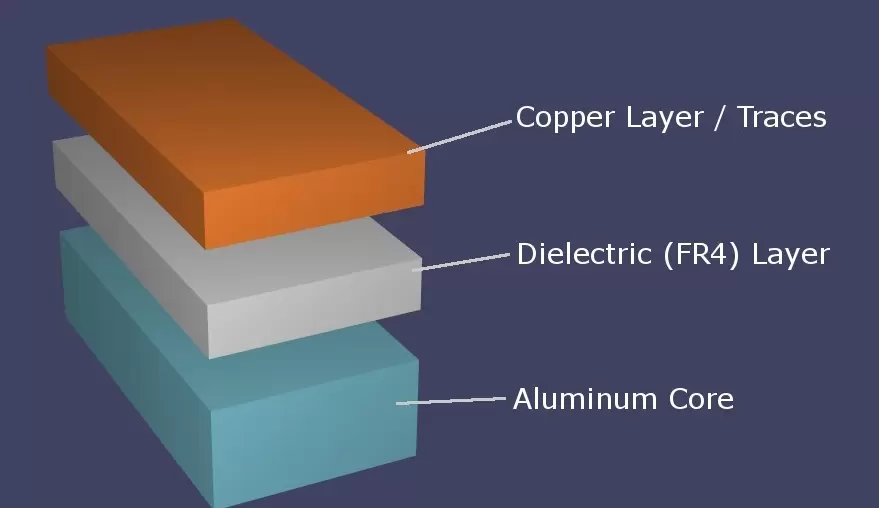
Disadvantages of Aluminum PCB
Limited Design Flexibility
Aluminum is a rigid material, making it unsuitable for flexible or bendable electronics (unlike flexible PCBs using polyimide substrates). Complex designs with intricate layers or fine-pitch components may also be challenging to fabricate due to aluminum’s structural constraints.
Lower Electrical Insulation
While the insulating layer (e.g., epoxy resin) between the circuit layer and aluminum substrate provides basic insulation, it offers lower dielectric strength than FR-4. This limits aluminum PCBs’ use in high-voltage applications (e.g., power grids) where strict insulation is required.
Higher Cost Than FR-4 for Low-Power Applications
For low-heat, low-power devices (e.g., simple sensors, small consumer electronics), aluminum PCBs are unnecessary and more expensive than standard FR-4 PCBs, as their heat dissipation benefits are underutilized.
Susceptibility to Galvanic Corrosion
When in contact with other metals (e.g., copper traces), aluminum may undergo galvanic corrosion if not properly insulated or coated. This requires additional protective measures (e.g., anti-corrosion coatings), adding to manufacturing costs.
Applications of Aluminum PCB
Aluminum PCBs are primarily used in scenarios where heat management is critical. Key applications include:
LED Lighting
High-power LEDs (e.g., streetlights, automotive headlights, industrial lighting) generate significant heat. Aluminum PCBs dissipate this heat efficiently, preventing LED burnout and ensuring consistent brightness.
Automotive Electronics
They are used in automotive components like engine control units (ECUs), LED taillights, and power inverters, where resistance to vibrations, heat, and harsh conditions is essential.
Power Electronics
Devices such as power supplies, inverters, and voltage regulators rely on aluminum PCBs to manage heat from high-current components (e.g., MOSFETs, diodes).
Aerospace and Military Equipment
In aerospace systems (e.g., avionics) and military devices, aluminum PCBs’ lightweight, durable, and heat-resistant properties make them ideal for withstanding extreme environments.
Consumer Electronics
They are found in devices like laptop chargers, audio amplifiers, and gaming consoles, where compact design and heat control are prioritized.

 en
en


 WhatsApp
WhatsApp