Ceramic PCB in Medical Devices: Reliability, Miniaturization & Safety
Introduction: Precision and Reliability in Medical Electronics
In medical technology, every microcircuit counts. Whether it’s a wearable heart monitor, implantable device, or diagnostic imaging system, medical electronics demand absolute precision, reliability, and safety. The circuit board must perform flawlessly under high temperature, humidity, and sterilization processes—all while ensuring patient safety.
This is where Ceramic Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) come into play. Built using advanced substrates such as Alumina (Al₂O₃), Aluminum Nitride (AlN), and Silicon Carbide (SiC), ceramic PCBs far outperform conventional FR-4 boards in thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, and biocompatibility.
With thermal conductivity up to 220 W/m·K, structural stability from –55°C to 800°C, and immunity to moisture and corrosion, ceramic PCBs are the backbone of modern high-reliability medical electronics.
Why Ceramic PCBs Lead in Medical Applications
The medical industry’s requirements are uncompromising—devices must be accurate, compact, sterilizable, and long-lasting. Traditional substrates like FR-4 fail to meet these standards under critical conditions. Ceramic PCBs, however, are engineered for these very challenges.
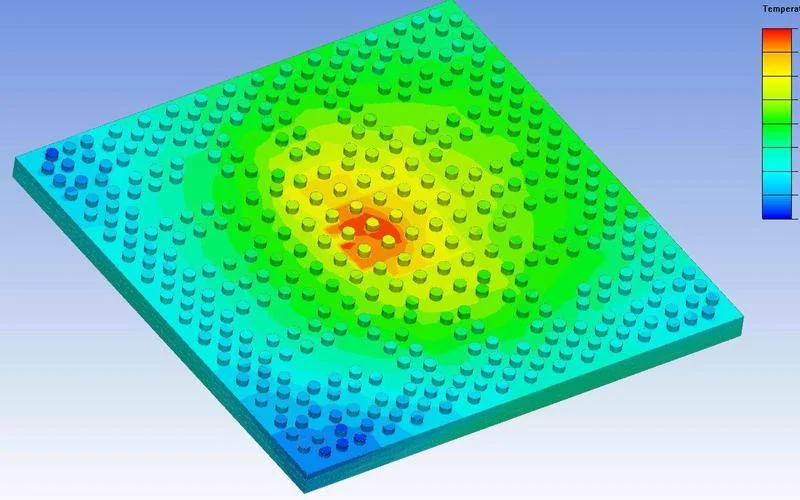
1. Unrivaled Thermal Management
Medical imaging systems, defibrillators, and laser surgical tools generate significant heat during continuous operation. AlN-based ceramic PCBs, with thermal conductivity up to 220 W/m·K, effectively dissipate heat from sensitive components such as power amplifiers and sensors.
This prevents overheating, ensuring consistent performance and extending the operational lifespan of medical electronics.
2. Extreme-Temperature and Chemical Stability
Medical devices must endure sterilization cycles—often above 120°C and involving strong disinfectants. Unlike organic laminates, ceramic substrates remain dimensionally stable and chemically inert. This makes Al₂O₃ and SiC ideal for reusable instruments and implantable sensors.
3. High-Frequency and Signal Precision
Many medical devices rely on high-frequency signal transmission, such as ultrasound probes or wireless telemetry units. Ceramic PCBs maintain a low dielectric constant (~8.8) and minimal signal loss, allowing accurate and noise-free signal delivery—critical for diagnostic accuracy.
4. Miniaturization and High-Density Interconnection (HDI)
Space is at a premium inside portable or implantable medical devices. Ceramic PCBs support fine-line circuit patterning and multilayer stacking using DPC (Direct Plated Copper) or thick-film printing techniques.
This allows engineers to integrate more functions into smaller footprints without sacrificing reliability—enabling truly miniaturized and lightweight medical designs.
5. Zero Degradation in Harsh Conditions
Ceramic PCBs resist humidity, UV radiation, and corrosive chemicals. Whether inside sterilization equipment or exposed to environmental stress in field diagnostics, their inorganic nature ensures no oxidation, delamination, or moisture absorption.
6. High Voltage and Current Reliability
In applications like X-ray imaging or defibrillator circuits, high voltages must be safely contained. Ceramic substrates’ dielectric strength (>15 kV/mm) ensures electrical isolation even under peak load conditions, minimizing the risk of short circuits or breakdowns.
Key Ceramic Materials for Medical Devices
Material | Thermal Conductivity | Dielectric Constant | Strengths | Typical Applications |
Alumina (Al₂O₃) | 18–30 W/m·K | 9.8 | Cost-effective, stable, corrosion-resistant | Diagnostic sensors, LED indicators |
Aluminum Nitride (AlN) | 140–220 W/m·K | 8.8 | Superior thermal performance, excellent dielectric insulation | Power modules, surgical lasers |
Silicon Carbide (SiC) | 120–180 W/m·K | ~10 | Extreme hardness, chemical inertness, mechanical resilience | Implantable devices, sterilization tools |
Each substrate is selected based on application needs—AlN for power-dense modules, Al₂O₃ for general instrumentation, and SiC for demanding sterilizable or implantable applications.
Manufacturing Techniques Ensuring Medical-Grade Precision
Producing medical-grade ceramic PCBs requires high-precision processes to meet regulatory and performance standards:
Direct Bonded Copper (DBC) – Bonds copper directly onto ceramic using high temperature, ensuring excellent heat transfer and adhesion.
Direct Plated Copper (DPC) – Deposits thin copper layers via sputtering and plating, enabling fine-line circuits for compact medical devices.
Thick-Film Printing – Integrates resistors, capacitors, and conductors directly onto ceramic, minimizing external components.
Laser Direct Imaging (LDI) – Creates micron-level circuit definition for miniaturized diagnostic and implantable devices.
Each process ensures low thermal resistance, strong metallization, and biocompatibility — essential for the reliability expected in medical devices.
Real-World Applications of Ceramic PCBs in Healthcare
Implantable Devices
Pacemakers, cochlear implants, and biosensors require materials that are biocompatible, corrosion-resistant, and electrically stable. Ceramic PCBs meet these criteria while maintaining miniature dimensions.
Diagnostic Equipment
MRI machines, ultrasound systems, and X-ray generators depend on stable high-voltage circuits. Ceramic boards prevent thermal drift and maintain signal clarity for accurate imaging.
LED-Based Surgical and Examination Lighting
Ceramic PCBs dissipate heat efficiently in high-intensity LED modules used for surgical illumination, ensuring brightness and longevity.
Patient Monitoring Systems
Wearable or bedside monitors use ceramic hybrid circuits for continuous operation without heat interference or electrical noise.
Laser and Electro-Surgical Instruments
AlN substrates provide superior heat management in laser scalpel drivers and power amplifiers, enhancing both precision and durability.
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
In the medical sector, product failure is not an option. Ceramic PCBs help manufacturers meet stringent regulatory requirements such as ISO 13485 for quality management and IEC 60601 for medical electrical equipment safety.
Their long-term stability and zero-toxic composition also support RoHS and REACH compliance, ensuring safety both for patients and medical personnel.
Why Choose Benlida for Medical Ceramic PCBs
Benlida Circuit is a trusted manufacturer of high-reliability ceramic PCBs, specializing in Al₂O₃, AlN, and SiC substrates. With precision DBC, DPC, and thick-film fabrication capabilities, Benlida provides medical OEMs with performance-optimized, biocompatible, and durable circuit solutions.
Whether developing implantable electronics, imaging systems, or portable medical devices, Benlida’s ceramic PCB expertise ensures consistent quality and reliability across every layer of production.
Learn more about Benlida’s medical-grade ceramic boards at Benlida’s Ceramic PCB page.
Conclusion
The medical field demands technology that operates flawlessly under the most critical conditions. With their unmatched thermal management, biocompatibility, and dimensional precision, ceramic PCBs are redefining reliability and safety in healthcare electronics.
As miniaturization and performance continue to advance, the role of ceramic PCB technology in enabling next-generation diagnostic, monitoring, and implantable devices will only grow.
Benlida Circuit remains a global leader in this evolution — transforming material science into medical innovation.

 en
en


 WhatsApp
WhatsApp